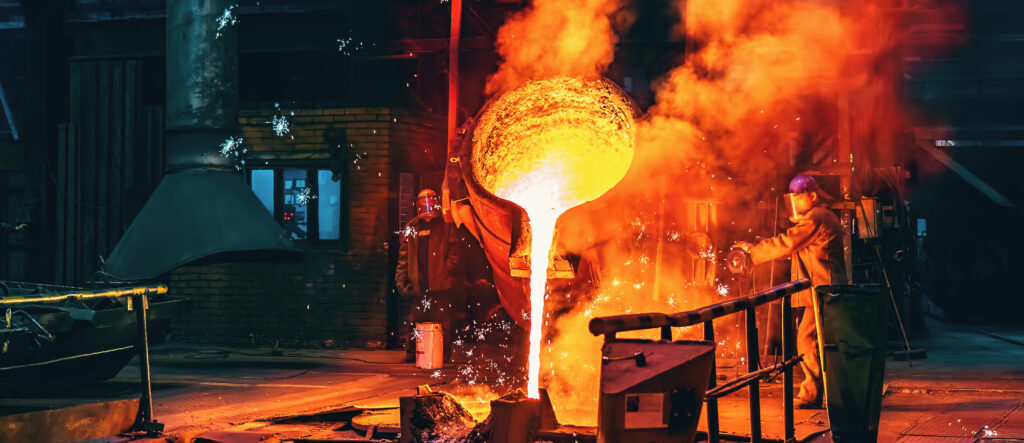
Foundries have long been trailblazers of craftsmanship, forging metals into essential components that fuel industries worldwide. However, as technology continues to evolve, so does the need for innovation within these industrial domains. The integration of 3D printing, emerges as a transformative force, poised to revolutionize traditional foundry practices.
Here’s why foundries should consider implementing 3D printing into their manufacturing processes:
Advantages of 3D Printing in Foundries
Enhanced Design Flexibility
3D printing unlocks unparalleled design freedom, allowing foundries to produce components with intricate geometries and complex structures that were previously unattainable using conventional methods. The technology enables the creation of parts with intricate internal features and customizable designs, offering unprecedented flexibility in product development.
Rapid Prototyping and Iteration
Time is of the essence in the competitive manufacturing landscape. 3D printing expedites the prototyping phase by facilitating swift iterations and adjustments to designs. Foundries can significantly reduce the time taken for design validation and refinement, accelerating the overall product development cycle.
Customized Tooling and Fixtures
Tailored tooling and fixtures are integral to optimizing foundry operations. 3D printing enables the cost-effective production of custom jigs, patterns, molds, and tooling with precision and speed. This customization enhances efficiency, reduces lead times, and ensures precise casting processes.
Complex Part Production
Foundries often encounter the challenge of manufacturing intricate components and intricate molds or cores. 3D printing excels in creating intricate parts with precise detailing and complex geometries. This capability allows foundries to expand their repertoire, catering to a broader range of complex part requirements with ease.
Material Versatility
The diversity of materials available for 3D printing continues to grow. Foundries can access specialized materials suited for high-temperature applications, durable tooling, or specific mechanical properties required for their components. This versatility empowers foundries to optimize material selection based on the intended use, enhancing the durability and performance of manufactured parts.
Key Considerations for Implementation
Assessing Feasibility and Use Cases
Foundries should evaluate their specific operational needs and identify areas where 3D printing can provide substantial improvements in efficiency, quality, or cost-effectiveness. Identifying initial use cases is crucial for successful implementation.
Technology Integration and Training
Integrating 3D printing requires investment in suitable equipment and expertise. Foundries should collaborate with experts to select the right printers, materials, and software while providing comprehensive training to personnel to ensure seamless adoption and utilization.
Pilot Projects and Continuous Improvement
Initiating pilot projects allows foundries to test the efficacy of 3D printing within their operations. Gathering feedback, analyzing outcomes, and refining strategies for continuous improvement are essential steps toward maximizing the potential of 3D printing.
The adoption of 3D printing represents a significant leap forward for foundries, offering a transformative path toward enhanced productivity, innovation, and competitiveness. Embracing this technology not only diversifies manufacturing capabilities but also positions foundries at the forefront of industry evolution. By integrating 3D printing into their processes, foundries can unlock a realm of possibilities, empowering them to create complex parts, streamline operations, and drive manufacturing excellence into the future. The journey from traditional manufacturing to additive manufacturing heralds a new era of limitless potential for foundries worldwide.
Share
Meet the Author